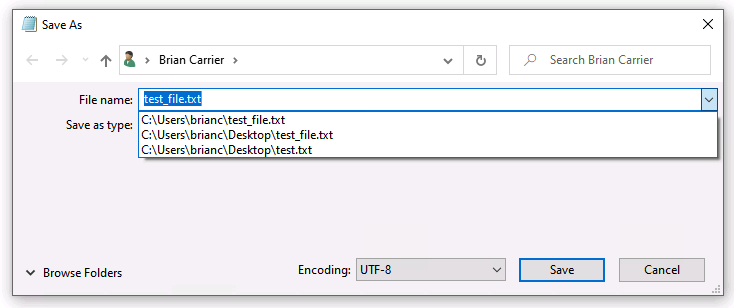
What Is a Windows OpenSave MRU Artifact?
The Windows OpenSaveMRU stores references to files that were selected by a user when using a standard Windows dialog to open or save a file.
It is in the “Data Accessed” artifact category, which stores what files a user opened.
Why Does a Windows OpenSave MRU Exist?
This data exists so that Windows can give a list of previously used file names. This feature makes it easier for users to re-use a name.
MRU stands for “Most Recently Used”.
How Is a Windows OpenSave MRU Useful in DFIR?
It is useful to a DFIR investigator because it can show what files the user was recently focused on:
- In an intrusion case with an account take over, this list could show what files the attacker was interested in. These could be documents with intellectual property or configuration files for their attack tools.
- For an insider threat case, it can show what kinds of documents the user was opening.
- In a general investigation, knowing what documents the user recently opened can reveal what they used the computer for.
It can also list file paths and times for files that have since been deleted or were on a removable drive.
Where Do You a Windows OpenSave MRU?
The OpenSave MRU data is stored in a User’s NTUSER.DAT registry hive. It’s in two different locations depending on the version of Windows. They both have the same structure, though, which is sub-keys based on the file extension, such as “docx”, “txt”, or “zip”.
Under each extension-based key, there is a list of file paths.
Since Windows Vista, the root key is found at HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\ComDLg32\OpenSavePidlMRU
Windows XP uses the following as the root key: HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\ComDLg32\OpenSaveMRU
What Does a Windows OpenSave MRU Contain?
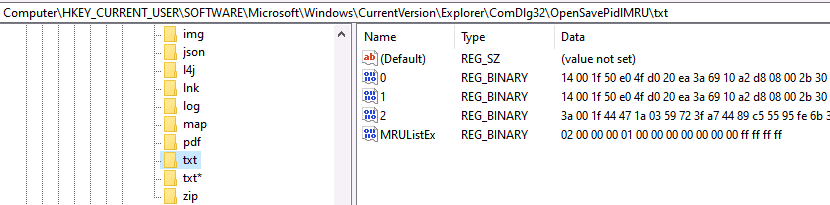
Since Windows Vista, each extension sub-key can contain up to 20 values. Their name is a counter (0 to 19) and the value is a binary structure that contains the path (and other data).
But, the path is not stored as an easy-to-read string. Instead, it is stored as a “PIDL”, which is a list of IDs that represent entries in a folder. The file name is stored in the value though in ASCII and UTF-16.
There is a “MRUListEx” value that contains an ordered list of counters (i.e. 0 to 19) that represent what order the files were last used. In the below example, you can see that two was the most recent, then 1, and then 0.
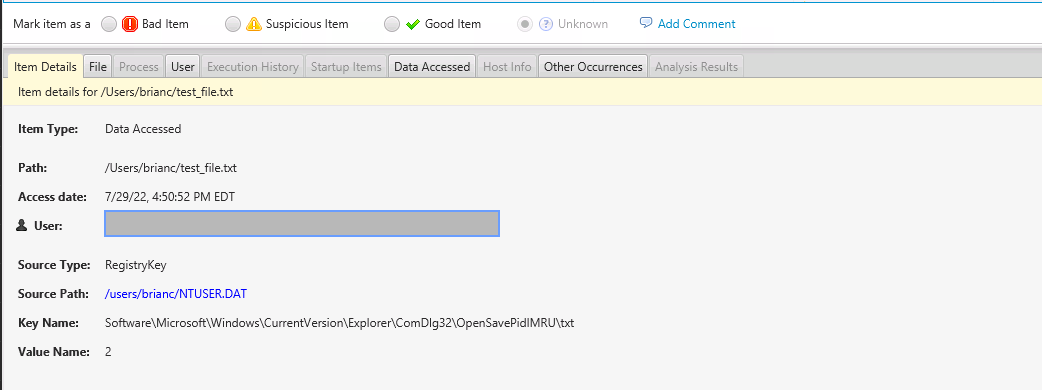
Where Can You See a Windows OpenSave MRU in Cyber Triage?
In Cyber Triage, you can find the OpenSave MRU contents in the “Data Accessed” section.
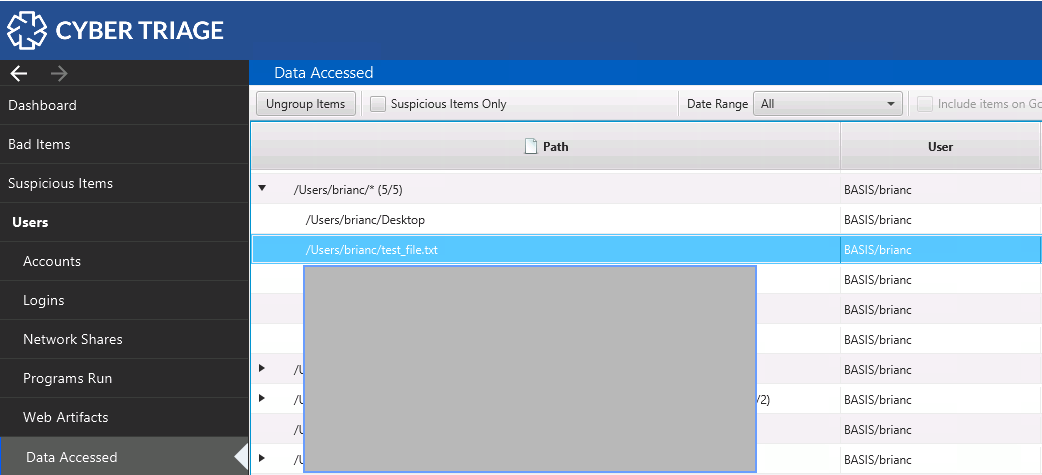
This section shows files that a user opened or saved. You can look at the Source Info section to see if the item came from an OpenSave MRU key or another artifact.
How Does Cyber Triage Score a Windows OpenSave MRU?
Cyber Triage will score Office and PDF files as suspicious if they have malware characteristics. For example, an Office document with a macro running when the document is opened would get flagged.
References
Watch
Subscribe To Cyber Triage Channel






