Cyber Triage 3.12 is out and we wanted to highlight a few key new features that will make your response faster.
- Data Exfiltration Detection: Quickly know if exfiltration tools or domains were used.
- USB Storage Identification: Quickly know if USB devices were recently used
- Server-side Disk Image Processing: More quickly process large batches of disk images
- Easier Artifact Validation: Compare Cyber Triage output with your current tools to know it’s getting what you need.
You can get the latest version from here or see the full list of changes in the User Manual.
A video from the Oct 9 webinar can be found here.
Quickly Identify Data Exfiltration
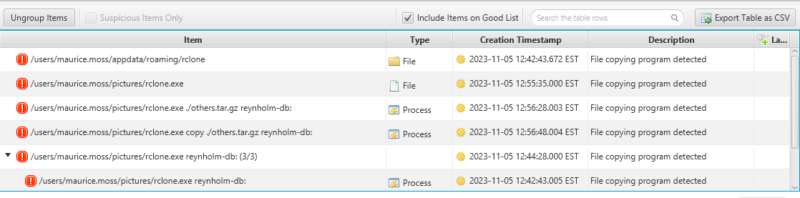
Data exfiltration occurs when data is removed from an organization’s network. It’s a risk to any organization because it can lead to sensitive data being obtained by a threat actor. Identifying if PII was leaked is a critical investigation goal of any DFIR team.
Cyber Triage makes this process easier by automatically flagging the use of tools and domains that can be used for data exfiltration, which means you will quickly see if there is suspicious exfiltration activity.
Attackers unfortunately will use legitimate data storage sites, such as GitHub or Google Drive to temporarily store data. Cyber Triage will now flag usage of those sites, but you can choose to “Good List” them if they are common in your environment.
Identify External Storage Usage
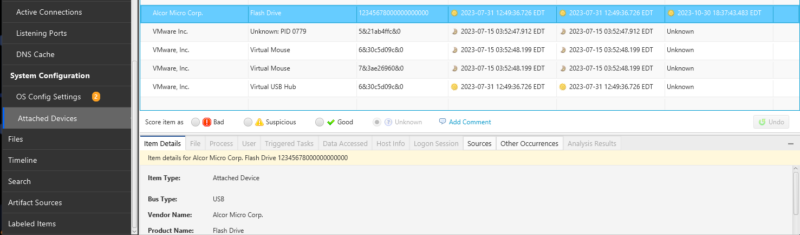
External USB storage can be used to exfiltrate data from an organization by employees or other authorized users. When investigating a user, it’s important to know if they have recently used USB devices.
Cyber Triage will now show USB devices that were attached to the system and when they were last connected. This can help you identify if there was recent USB activity on the system. You can find these results in a new “Attached Devices” section.
Server-side Disk Image Processing
Processing large amounts of data quickly is important to get your first clues ASAP. Cyber Triage historically required Team clients to stay online while the disk images underwent an initial processing because the disk images were only on the client. This limited what else the investigators could do until all of them were initially scanned.
Cyber Triage can now process disk images and Collector output (JSON files) on the server, if the server already has access to the data source. The client can then disconnect and perform other tasks.
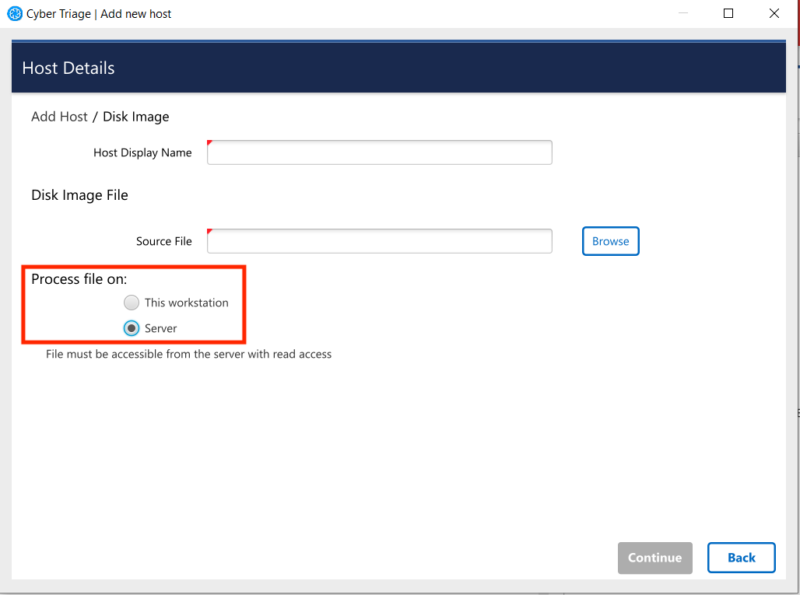
To use this feature, your server needs access to the disk images and the client simply submits the path to the server for it to schedule.
More Easily Validate Your Results
It’s important to validate the results of any forensics tool. To make investigations faster, Cyber Triage has chosen to do things differently, which has made validation more complicated.
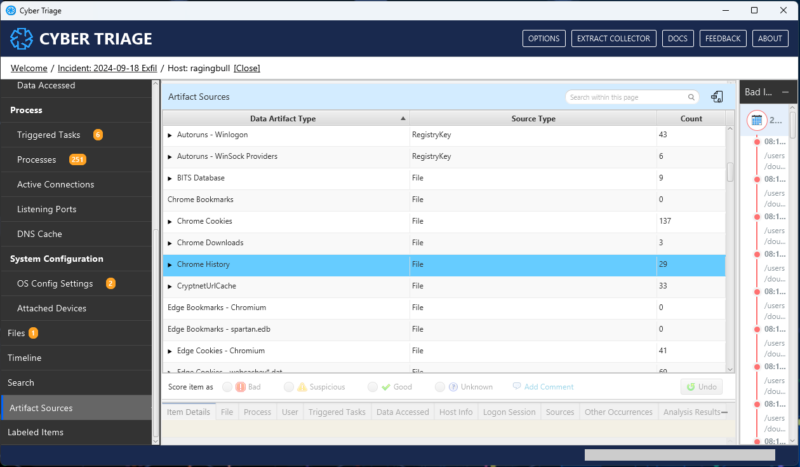
For example, investigators frequently wanted to compare results from parsing Prefetch. This was difficult to do with Cyber Triage because we never had a place to show just “Prefetch”. We show Prefetch as a process, because it indicates a process and we don’t want you to always have to memorize what every artifact means. We would always show you in the “Sources” view though that it came from Prefetech.
Cyber Triage as a new “Artifact Sources” view that is organized by the traditional data artifacts and lets you see what Cyber Triage found from that source. You can see all processes created from Prefetch.
Our assumption is that this view will be primarily during evaluations and in the first weeks of using Cyber Triage. Then they will use our more traditional way of grouping artifacts.
Try It Now
You can try the latest Cyber Triage now using this link.